Previous
Art therapist
You'll need a degree in Diagnostic Radiography or Diagnostic Imaging to become a diagnostic radiographer in the NHS. In Scotland, 3 universities offer pre-registration degree programmes.
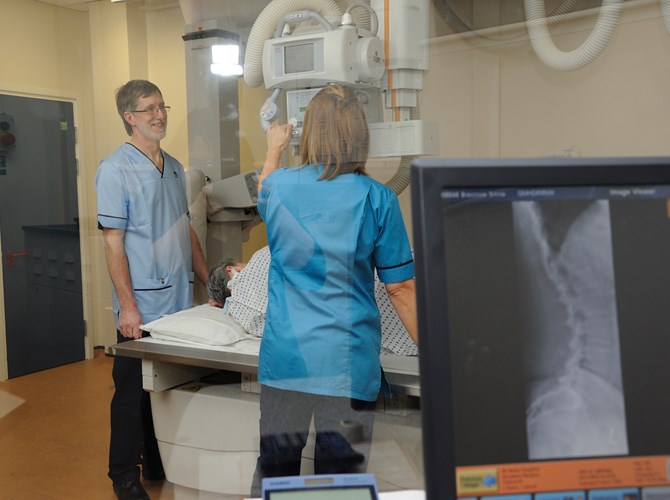
Diagnostic radiographers play a key role in large medical teams. Using the latest imaging technology, they take high-quality images of the inside of the body. These images are used to diagnose and monitor illnesses or injuries so patients receive the correct treatment.
To work in the NHS, diagnostic radiographers must be registered with the Health and Care Professions Council (HCPC).
To get on a college or university course that could lead to a career as a diagnostic radiographer, useful subjects include:
Speak to your guidance teacher about subjects offered at your school.

You may find it helpful to get some healthcare experience by doing a work placement or volunteering. You’ll get training, increase your knowledge, and learn new skills. This could help you when applying to university, college or a new job with NHSScotland.
You'll need a degree to become a diagnostic radiographer. Most universities accept a wide range of qualifications, giving you the option of applying directly from school or going to college first. At college, you could do an HNC in a science-based subject before applying to university to do an undergraduate programme.
The degree programme you choose must be approved by the Health and Care Professions Council.
You should contact individual universities to find out about specific entry requirements.
Widening participation supports adult learners who want to go to university. If you’re an adult with few or no qualifications, you could get into higher education through the Scottish Wider Access Programme (SWAP). Many universities also provide access programmes to help you get the degree entry qualifications you need.
Three universities in Scotland offer degree courses in Diagnostic Radiography or Diagnostic Imaging:
Pre-registration undergraduate programmes take 4 years full-time.
If you already have relevant qualifications and healthcare experience, you can do a postgraduate diploma or master's in Diagnostic Radiography. Pre-registration postgraduate programmes usually take 2 years.
As a diagnostic radiographer, you’ll take images using different imaging techniques, such as:
Your expert knowledge and skills would be used to identify injuries and illnesses, including cancers or coronary artery disease.
Tasks include:
You'll need these skills:
You’ll also need to use technical, computerised imaging equipment with good hand-to-eye coordination. You must also keep up to date with new imaging techniques and technologies.
Diagnostic radiographers work with other healthcare professionals, including:
You could work in:
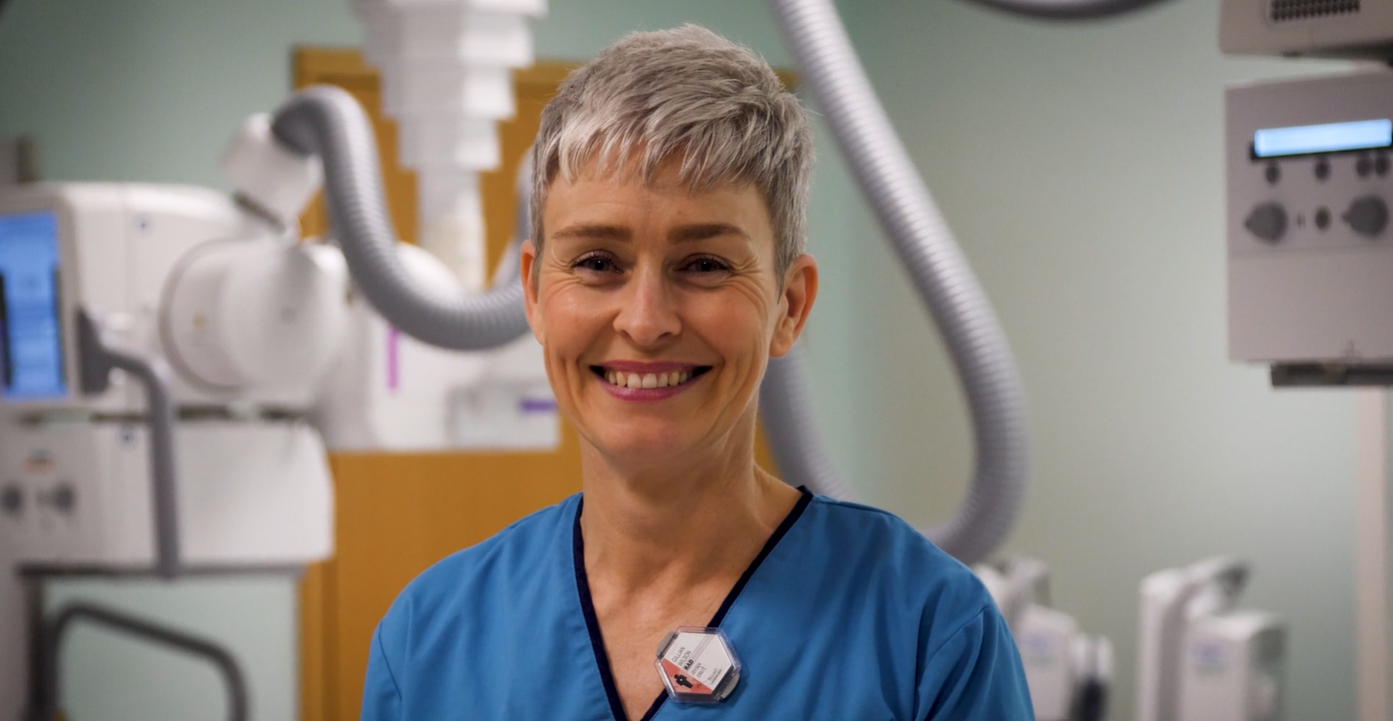

Check out our 360 videos to learn more about the role of a diagnostic radiographer.
You'll get to meet Gillian, a diagnostic radiographer at the Golden Jubilee National Hospital. Find out how she uses lots of different imaging technology to produce images of the body.
During your career, you'll have to keep your skills and knowledge up to date with Continuing Professional Development (CPD). The Society and College of Radiographers (SCoR) provides courses, conferences and seminars where you can exchange ideas and update your skills.
You may choose to specialise in a particular type of imaging, such as MRI or sonography. Some diagnostic radiographers work with specific patient groups, such as:
You could also move into management, either within radiography services or general management. There is also the option to consider a career in research, education, or within the independent sector.
When you become a qualified diagnostic radiographer, you must register with the HCPC to work in the NHS. You can also join the Society and College of Radiographers (SCoR).

Discover the range of AHP careers you can choose in the NHS.
Allied health professions
Our blog includes how-to guides, case studies, and career resources.
Discover more